HOW DO WATER SOFTENERS WORK?
There is a lot of confusion surrounding water softeners and how they operate. Many individuals who come to Sawtooth Inc. looking for a new unit or repairs to existing systems are unclear on why a water softener uses salt, what the difference between a salt-free water conditioner and a salt-based water softener is, and why there are so many different configurations and price ranges for water softening units.
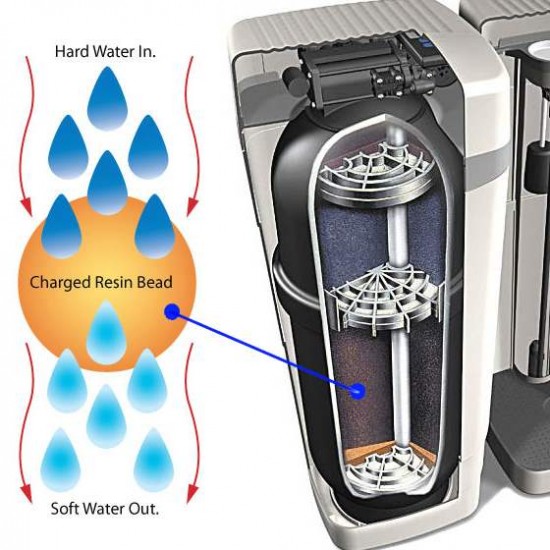
Every water softener that uses salt has a tank that stores a material called RESIN. Resin is a man-made material that if put under a microscope looks very similar to a chain-link fence that has been wound into a ball or bead. A water softener is filled with these little beads in various amounts depending on the size of the system. Salt is used to “charge” these beads so that the resin can remove hardness minerals from your water.
As hard water (water that is mixed with the naturally occurring minerals calcium and magnesium) flows through the RESIN BEADS, an exchange takes place. The sodium on the resin beads and the hardness minerals trade places. This process is known as ION EXCHANGE. In short, water mixed with calcium and magnesium comes into the water softener, and water mixed with salt comes out.
The most common unit of measure for hardness is GRAINS or GRAINS PER GALLON (gpg). The hardness of a water supply is easily measured and commonly done for free by water treatment professionals. The hardness measurement is used to determine a water softener’s SOFTENING CAPACITY, or, how much hard water can pass through a softener before the resin beads can no longer soften water and need to be cleaned. The process of cleaning resin beads is know as REGENERATION.

Unlike a conventional filter like those found in fridges or drinking water systems that collect contaminants and then have to be replaced periodically, RESIN inside water softeners can filter hardness minerals over and over again without being replaced. This process is called REGENERATION. The frequency and length of the regeneration cycle depends on the size of the unit, the valve and the computer.
Regeneration is essentially a self-cleaning process that occurs repeatedly throughout the life-time of the water softener. The valve and computer work in tandem to introduce water in with salt to create a brine solution. The resin is then rinsed and coated with this brine so that the exchange process between salt and the hardness minerals can occur over and over again.
There are many variables that go into determining how long the regeneration cycle lasts, how much water will be used to rinse or clean the resin and how much dissolved salt will be used to “charge” the resin. Some water softeners are incredibly inefficient at this process, wasting thousands of gallons of water and hundreds of pounds of salt over their lifetime.

A major point of confusion when purchasing a water softener is whether to buy a salt-based unit or a salt-free system. Many people are under the impression that salt-free water conditioners do the exact same thing as a salt system. This is not the case. Salt-free water conditioners CONVERT the hardness minerals into a different substance, they do not actually REMOVE the hardness minerals from the water supply like a salt-based unit.
Salt-free water conditioners come in a variety of configurations. Some use magnetic, catalytic, electric or an electro-dialysis process to convert hardness minerals. There are even systems that use citric acid to accomplish this conversion.
At Sawtooth Inc., we have salt-free options available; however, in our experience these units will only keep plumbing pipe clear of hardness buildup. These units do not provide the other benefits that a salt-based unit will provide such as softer skin and clothes, brighter dishes, faucets and fixtures that are free from buildup etc.

When shopping for a water softener you will be bombarded by dozens of different brands, each with their own unique appearance; however, we recommend ignoring the aesthetic components and focus specifically on function.
There are four different types of water softener configurations commonly found in the Southern Idaho market:
- Single media tank — This is the most common, least expensive, and most problem-prone configuration. It utilizes a single filtration tank that holds the softening resin, and either a separate holding tank that stores salt, or the salt will be poured in together with the filtration tank inside a single plastic cabinet. Most big-box stores sell this type of unit (Kenmore, Whirpool, GE etc.).
- Single media tank with mixed media — Less common than #1 because of the price difference. The filtration tank not only has resin inside but other filtering material (media) to reduce other contaminants from the water.
- Double media tanks — This design is essentially two softeners plumbed together into a single unit for 24/7 soft water. This configuration is most commonly used for commercial applications; however, some residential brands come this way out of the box (most expensive water softening option).
- Single media tank with compartments — Similar to #2 except that the filtering media is not mixed together. The single tank is separated into compartments by screens. Each compartment holds a different filtering media to not only soften water but purify as well for the entire home (best type of unit for overall water quality, efficiency and cost-to-performance).